To study horses and their skeletal and muscular makeup, you need to understand their anatomy and physiology. This involves studying their bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Horse anatomy and physiology are essential for those interested in equine sciences, veterinary medicine, and horse training. The skeleton and muscular system of horses are vital for movement, balance, and performance. Students in these fields need to have a detailed understanding of the horse’s anatomy and physiology to diagnose and treat injuries or illnesses correctly. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of horse anatomy and physiology, how to study it, and its importance in equine sciences, veterinary medicine, and horse training. With this knowledge, you will be able to appreciate these magnificent animals’ physical abilities and understand how they move and function.
Credit: www.etsy.com
Understanding Horse Anatomy
Horses are fascinating creatures with a unique anatomy that sets them apart from other mammals. Knowing the horse’s skeletal and muscular makeup is crucial for anyone who wants to study horses, from veterinarians to trainers. Understanding horse anatomy enables you to identify any abnormalities in a horse’s physical structure that may affect its performance and health.
Here is an overview of horse anatomy and its key components.
Overview Of Horse Anatomy And Its Key Components
- Horses are herbivores that belong to the equus genus.
- Horses have a large, round head with long ears on top.
- The neck, back, and legs must be evaluated carefully to determine a horse’s physical health.
- The horse’s anatomy comprises two essential components, the skeletal system and the muscular system.
The skeletal system provides the rigid framework for the horse’s body, while the muscular system enables it to move. Understanding the horse’s skeletal structure is essential for evaluating its physical health.
Detailed Explanation And Visual Representation Of The Horse’S Skeletal Structure
Skull
The horse’s skull has a large toothless gap at the front of the mouth, which facilitates grazing. A horse skull has 34-36 teeth for shearing, tearing, and grinding food. The skull contains openings for the eyes, nostrils, and ears.
Neck
Horses’ necks are long and flexible, containing seven cervical vertebrae. The neck provides significant support for the horse’s head and enables it to adjust its balance during movement.
Spine
A horse’s spine has several sections, the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions, and the sacrum and coccyx. The spine provides support and flexibility to the horse’s back, allowing it to flex and extend its torso during movement.
Ribs
Horses have 18 pairs of ribs that attach to the thoracic vertebrae and the sternum, forming a sturdy chest structure. The ribs play a crucial role in protecting the horse’s internal organs, including the lungs and heart.
Legs
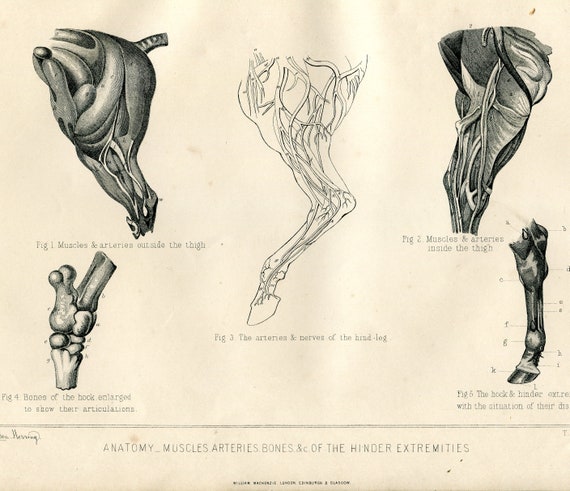
Horses have long, slender, and powerful legs that enable them to run, jump, and kick. Their forelegs consist of the shoulder blade, upper arm, forearm, knee, cannon bone, pastern, and hoof. Their hind legs have a more complex structure, consisting of the femur, tibia, fibula, hock, cannon bone, pastern, and hoof.
Hooves
A horse’s hoof is a complex structure made up of the hoof wall, sole, and frog. The hoof wall is the hard, outer layer that encases the sensitive internal structures of the hoof, such as the laminae, sole, and frog.
Understanding the horse’s muscular structure is equally important as the skeletal system. Horses owe their speed, agility, and strength to their musculature.
Detailed Explanation And Visual Representation Of The Horse’S Muscular Structure
Major Muscle Groups And Their Functions
- The shoulder muscles are responsible for moving the forelimb.
- The croup muscles are the largest and most powerful hindlimb muscles that enable the horse to push off the ground and propel forward.
- The neck muscles are essential for bending, flexing, and extending the horse’s neck.
- The muscles in the barrel and lower back area help to support and manipulate the horse’s back.
- The leg muscles work together to support the horse’s weight, enabling it to move quickly and powerfully.
By understanding the horse’s anatomy, you can provide better care for your horse by identifying potential problems before they become severe. Any horse lover should have a basic understanding of horse anatomy to appreciate and care for these magnificent creatures.
Methods And Techniques For Studying Horse Anatomy
Horses have been an essential part of human life since ancient times. Humans have domesticated them for transportation, agriculture, and sports. A deeper understanding of their skeletal and muscular makeup can help improve equine health and performance. In this blog post, we will dive into the different methods and techniques used for studying horse anatomy.
Overview Of Different Methods For Bone And Muscle Structure Analysis
Several methods can be used to study the bone and muscle structure of horses.
- Autopsies: postmortem examination of a horse’s anatomy can provide detailed information about its bone and muscle structure.
- X-rays: this non-invasive method uses radiation to create images of the horse’s bones.
- Ct scans: computed tomography scans provide cross-sectional images of the horse’s body, allowing for more detailed analysis of the skeletal and muscular system.
- Ultrasound imaging: this technique uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs, muscles, and tissues.
Detailed Explanation Of How To Examine A Horse’S Anatomy Through Palpation And Manipulation
Palpation and manipulation techniques can help veterinarians, trainers, and researchers identify areas of pain or discomfort and diagnose potential injuries.
Palpating The Muscles
- Start at the forelimb: palpate the horse’s shoulder muscles while standing next to it. Move to the forearm, elbow, and knee muscles.
- Move to the hindlimb: start at the hip muscles, move down to the hock muscles and then palpate the stifle, the gaskin, and the muscles of the lower leg.
- Hand-walking: observe the horse’s movement while walking it. This will help identify any areas of muscle stiffness, pain, or lameness.
Palpating The Skeleton
- Check the neck and withers: palpate the spine and spinous processes, and observe the horse’s reaction to localized pressure.
- Move to the fore and hindlimbs: palpate the joints, tendons, and ligaments. Carefully flex and extend the limbs to identify any areas of discomfort or pain.
- Observe the horse while exercising to check for any asymmetry.
Discussion Of Emerging Technologies And Techniques In Horse Anatomy Research
Technology is advancing rapidly, leading to new techniques for studying horse anatomy.
- 3d printing: using 3d printers, researchers can create accurate models of horse anatomy that can be used for training veterinary students, analyzing injuries, and planning surgeries.
- Virtual reality: virtual reality programs help students and researchers interact with 3d models of horse anatomy, providing a better understanding of the skeletal and muscular systems.
A thorough understanding of horse anatomy can help improve horse health, performance, and rehabilitation. By using a combination of methods, techniques, and emerging technologies, we can continue to improve our knowledge of equine anatomy.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Study Horses And Their Skeletal And Muscular Makeup?
What Are The Basic Skeletal And Muscular Structures Of A Horse?
The horse’s skeleton is composed of the skull, spine, ribs, and limbs. The limbs are supported by muscles, such as the pectorals, gluteals, and quadriceps. The limbs are highly specialized to support the weight of the animal and to allow it to move quickly over various surfaces.
How Can Identifying Different Muscle Groups In Horses Help With Their Training And Performance?
Identifying different muscle groups in horses can help improve their training and performance. Knowing which muscles to strengthen and stretch can enhance their flexibility, coordination, and overall athletic abilities. Proper muscle conditioning can also prevent injuries and improve recovery times.
What Are Some Common Issues With A Horse’S Skeletal And Muscular Structure And How Can They Be Prevented Or Treated?
Common issues with a horse’s skeletal and muscular structure are lameness, joint problems, and muscle soreness. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and proper care can prevent these issues. Treatment options include rest, medication, physical therapy, and surgery if necessary. Consultation with a veterinarian is recommended.
What Tools Or Equipment Are Necessary For Studying A Horse’S Skeletal And Muscular Makeup?
The necessary tools for studying a horse’s skeletal and muscular makeup include x-ray machines, ultrasound equipment, magnetic resonance imaging (mri), and endoscopes. These tools are used to capture images of the horse’s bones, muscles, and organs to aid in diagnosis and treatment.
How Can Understanding A Horse’S Skeletal And Muscular Structure Help With Breeding And Genetics?
Understanding a horse’s skeletal and muscular structure helps with breeding and genetics by allowing breeders to select horses with optimal physical traits. Knowledge of skeletal and muscular anatomy can also aid in reducing injuries and improving horse performance.
Where Can I Find Reputable Resources For Studying Horses And Their Anatomy?
To find reputable resources for studying horse anatomy, visit equine veterinary colleges, horse anatomy textbooks, and equine anatomy websites. Online courses and youtube videos are also sources of information.
Conclusion
Studying the skeletal and muscular anatomy of horses is crucial for horse enthusiasts, horse trainers, and veterinarians. By understanding the intricacies of equine anatomy, you can better comprehend horse behavior, diagnose and treat injuries, and design effective training programs. Remember that horses are unique animals, and their musculoskeletal system plays a critical role in their overall performance.
Therefore, it is essential to observe horses carefully and educate ourselves on their structure and function. Furthermore, hands-on learning, such as dissections, will increase our understanding of equine anatomy. Additionally, technology such as advanced imaging techniques can aid in identifying potential issues in horses.
By combining these resources and techniques, we can better appreciate and care for horses to ensure their optimal health, wellness, and performance.




